26 Apr Calonectria
Calonectria De Not., Comm. Soc. Crittog. Ital. 2(fasc.3): 477 (1867)
For synonyms see Index Fungorum (2018)
Background
Calonectria was first introduced based on C. daldiniana in 1867. Calonectria species are pathogenic to a wide range of woody and herbaceous plant hosts in tropical and subtropical areas (Chen et al. 2011; Crous 2002; Lechat et al. 2010; Lombard et al. 2010 a,b; Li et al. 2017). The sexual morphs of Calonectria are characterised by yellow to dark red ascomata, with scaly to warty walls, and clavate, 4–8-spored asci. They produce Cylindrocladium asexual morphs with branched conidiophores, cylindrical, septate conidia, and stipe extensions with terminal vesicles (Crous 2002; Lombard et al. 2010b, 2016; Li et al. 2017).
Classification – Sordariomycetes, Hypocreaomycetidae, Hypocreales, Nectriaceae
Type species – Calonectria pyrochroa (Desm.) Sacc., Michelia 1(no. 3): 308 (1878)
Distribution –– Worldwide
Disease Symptoms – Box blight, Cutting rot, Damping off, Canker, Leaf spots, leaf and shoot blights, Red crown rot, Root rot
Species of Calonectria are capable of causing diseases in all plant parts. Most diseases have been recorded from young plants or recent field plantings. Symptoms vary according to host species, host age or developmental stage, environmental conditions and the Calonectria species itself (Barnes and Linderman 2001). Leaf spots (caused by C. colhounii, C. ilicola, C. indusiata and C. pteridis) first appear as water-soaked lesions turning tan to dark brown, circular or irregular in shape surrounded by a red, dark brown or purple border with a chlorotic zone. Root necrosis is the main symptom of root rot caused by species such as C. crotalariae and C. ilicola (Lombard et al. 2010a, 2011). On conifers, there is necrosis of lateral and primary roots accompanied with blacking and splitting of the root cortex while on hardwoods, there is blackening of the root cortex with longitudinal cracking (Cordell et al. 1975). Lesions may coalesce and completely destroy the root. Crown infection can occur with the spread of root infection leading to stunting, discolouration of foliage, defoliation and plant death (Lombard et al. 2010a; Lombard et al. 2011).
Hosts – Calonectria species are soil-borne pathogens and are mainly associated with forestry, agricultural and horticultural plants, on more than 100 plant families (Chen et al. 2011; Crous et al. 1991; Crous 2002, Gehesquiére et al. 2016; Lombard et al. 2010a, b; Li et al. 2017; Lopes et al. 2018). Calonectria species are less commonly associated with fruit rot as compared to leaf spot and root rot (Diaz et al. 2013; Lopes et al. 2018).
Morphological based identification and diversity
Calonectria species were known by Cylindrocladium names for many years. Cylindrocladium species were commonly found in nature and well-known plant pathogens. Later Calonectria was conserved (Hawksworth 2011; McNeill et al. 2012) over Cylindrocladium by Rossman et al. (2013). Most isolates were identified based on morphology. Later, polyphasic approaches based on morphology and sexual compatibility was used to delimit cryptic species (Schoch et al. 2001; Lombard et al. 2010a, b, 2016) and these studies have revealed that there are many species of Calonectria yet to be discovered (Lombard et al. 2016). Calonectria has been subjected to numerous taxonomic studies and 129 species have been recognized based on both morphological and molecular approaches (Crous and Wingfield 1994; Crous 2002; Lechat et al. 2010; Li et al. 2017; Lombard et al. 2010a, b, 2016; Maharachchikumbura et al. 2015, 2016; Lopes et al. 2018).
Macroconidial dimensions and septation, and shape of the vesicle are the best diagnostic characters for identification of Calonectria (Schoch et al. 2000; Crous 2002; Li et al. 2017). Perithecial colour, ascospore number within the asci, and ascospore septation and dimensions are also important for sexual morph identification (Lombard et al. 2010a). However, perithecia of Calonectria species are morphologically very similar, hence are not useful in identification (Crous and Wingfield 1994; Crous 2002). However, intraspecific variation in vesicle shape and conidial dimensions are commonly used in the identification of Calonectria, which can result in taxonomic confusion (Crous et al. 1998; Lombard et al. 2010b).
Molecular based identification and diversity
Morphological data are essential to supplement DNA sequence data for accurate species identification (Lombard et al. 2016). Earlier studies used ITS gene alone to separate Cylindrocladium species, however, the ITS region contains few informative characters (Crous et al. 1999; Schoch et al. 2001; Lombard et al. 2010b). A genus-wide phylogeny can be inferred using TUB, TEF1-α, cmdA and His3 (Lombard et al. 2016; Crous et al. 2002). The LSU gene also provides little information in resolving species of the genus (Lombard et al. 2010b). This study reconstructs the phylogeny of Calonectria based on analyses of a combined TEF1-α, TUB, cmdA and His3 sequence data. After Lombard et al (2010a), this is the first multigene analysis for all the available Calonectria species. Calonectria species formed two major clades in our phylogenetic analysis, which define morphologically similar groups. Similar results were obtained in the previous study by Lombard et al. (2010b) employing seven gene regions (including additional LSU, ITS and ACT sequence data). However, insufficient data are available for the His3 gene region in GenBank. Therefore, it is difficult to have comparative phylogenetic analyses.
Recommended genetic markers (genus level) – LSU and ITS
Recommended genetic markers (species level) – TUB, TEF1-α, cmdA, His3, ACT
Accepted number of species: There are 399 species epithets in Index Fungorum (2018) under this genus. However, only 283 are accepted.
References: Lombard et al. 2010a, b, c, d, 2016, Maharachchikumbura et al. 2015, 2016 (morphology and phylogeny)
Table Calonectria. Details of the isolates used in the phylogenetic tree. Ex-type (ex-epitype) strains are in bold and marked with an * and voucher strains are in bold.
| Species | Isolate | TEF1- α | His3 | cmdA | TUB |
| Calonectria acicola | CBS 114812* | GQ267291 | DQ190692 | GQ267359 | DQ190590 |
| C. aciculata | CMW 47645*; CERC 5342; CBS 142883 5342; CBS 142883 |
MF442644 | MF442759 | MF442874 | MF442989 |
| C. aconidialis | CBS 136086* | KJ462785 | KJ463133 | KJ463017 | — |
| C. amazonica | CBS 116250*; CPC 3534 | KX784682 | — | KX784555 | KX784612 |
| C. amazoniensis | CBS 115440*; CPC 3885 | KX784685 | — | KX784558 | KX784615 |
| C. angustata | CBS 109065*; CPC 2347; CBS 114544 | FJ918551 | DQ190696 | GQ267361 | AF207543 |
| C. arbusta | CBS 136079*; CMW 31370; CERC1705 | KJ462787 | KJ463135 | KJ463018 | — |
| Ca. asiatica | CBS 114073*; CMW 23782; CBS 112954 SFE 726; CPC 3900 |
AY725705 | AY725658 | AY725741 | AY725616 |
| C. australiensis | CBS 112954* | GQ267293 | DQ190699 | GQ267363 | DQ190596 |
| C. avesiculata | CBS 313.92*; CMW 23670; CPC 2373; ATCC 38226 | GQ267294 | — | GQ267364 | — |
| C. blephiliae | CBS136425*; CPC21859 | KF777243 | — | — | KF777246 |
| C. brachiatica | CBS 123700*; CMW 25298 | GQ267296 | FJ696396 | GQ267366 | FJ696388 |
| C. brasiliensis | CBS 230.51*; CMW 23670; CPC 2390 | GQ267328 | GQ267259 | GQ267421 | GQ267241 |
| C. brassiana | CBS 134855*; CBS 13485 | KM395883 | — | KM396057 | KM395970 |
| C. brassicae | CBS 111869*; CMW 30982; CPC 2409; PC 551197 | FJ918566 | DQ190720 | GQ267382 | AF232857 |
| C. brassicicola | CBS 112841*; CPC 4552 | KX784689 | — | KX784561 | KX784619 |
| C. brevistipitata | CBS 115671*; CPC 94 | KX784693 | — | KX784565 | KX784623 |
| C. canadiana | CBS 110817*; CPC 499 | GQ267297 | — | AY725743 | AF348212 |
| C. candelabrum | CPC 1675 | FJ972525 | — | GQ267367 | FJ972426 |
| C. cerciana | CBS 123693*; CMW 25309 | FJ918559 | FJ918528 | GQ267369 | FJ918510 |
| C. chinensis | CBS 114827*; CMW 23674; CPC 4101 | AY725710 | AY725661 | AY725747 | AY725619 |
| C. citri | CBS 186.36*; CMW 23675 | GQ267299 | GQ267371 | GQ267247 | AF333393 |
| C. clavata | CBS 114557*; ATCC 66389; CPC 2536 | GQ267305 | DQ190623 | GQ267377 | AF333396 |
| C. cliffordiicola | CBS 111812*; CPC 2631 | KX784694 | — | KX784566 | KX784624 |
| C. colhounii | CBS 293.79*; CMW 30999 | GQ267301 | DQ190639 | GQ267373 | DQ190564 |
| C. colombiana | CBS 115127*; CMW 30871; CPC 1160 | FJ972492 | FJ972442 | GQ267455 | FJ972423 |
| C. colombiensis | CBS 112220*; CMW 23676; CPC 723 | AY725711 | AY725662 | AY725748 | GQ267207 |
| C. crousiana | CBS 127198*; CMW 27249 | HQ285822 | — | — | HQ285794 |
| C. curvispora | CBS 116159*; CMW 23693 | GQ267302 | AY725664 | GQ267374 | AF333394 |
| C. cylindrospora | CBS 110666; CPC 496 | FJ918557 | FJ918527 | GQ267423 | FJ918509 |
| C. densa | CBS 125261*; CMW 31182 | GQ267352 | — | GQ267444 | GQ267232 |
| C. duoramosa | CBS 134656*; LPF434 | KM395853 | KM396110 | KM396027 | KM395940 |
| C. ecuadorensis | CBS 111706* | KX784747 | — | KX784604 | KX784674 |
| C. ecuadoriae | CBS 111406*; CPC 1635 | GQ267303 | DQ190705 | GQ267375 | DQ190600 |
| C. ericae | CBS 114458*; CPC 2019 | KX784699 | — | KX784571 | KX784629 |
| C. eucalypti | CBS 125275* | GQ267338 | GQ267267 | GQ267430 | GQ267218 |
| C. eucalypticola | CBS 134847* | KM395877 | — | KM396051 | KM395964 |
| C. expansa | CBS 136247*; CMW 31392; CERC 1727 | KJ462798 | KJ463146 | KJ463029 | KJ462914 |
| C. foliicola | CBS 136641*; CMW 31393; CERC 1728 | KJ462800 | — | KJ463031 | KJ462916 |
| C. fujianensis | CBS 127201*; CMW 27257 | HQ285820 | HQ285806 | — | HQ285792 |
| C. glaebicola | CBS 134852* | KM395879 | KM396136 | KM396053 | KM395966 |
| C. gordoniae | CBS 112142*; CPC 3136; ATCC 201837 | GQ267309 | DQ190708 | GQ267381 | AF449449 |
| C. gracilipes | CBS 111141* | GQ267311 | DQ190644 | GQ267385 | DQ190566 |
| C. gracilis | CBS 111807* | GQ267323 | DQ190646 | GQ267407 | AF232858 |
| C. guangxiensis | CBS 136092*; CMW 35409; CERC 1900; CPC 23506 | KJ462803 | KJ463151 | KJ463034 | KJ462919 |
| C. hainanensis | CBS 136248*; CMW 35187; CERC 1863 | KJ462805 | KJ463152 | KJ463036 | — |
| C. hawksworthii | CBS 111870*; CPC 2405; MUCL 30866 | FJ918558 | DQ190649 | GQ267386 | AF333407 |
| C. henricotiae | CBS 138102*; CB045 | — | KF815185 | KF815157 | JX535308 |
| C. hodgesii | CBS 133609*; LPF 245 | KC491225 | — | KC491222 | KC491228 |
| C. honghensis | CMW 476695*; CERC 5572; CBS 142885 | MF442665 | MF442780 | MF442895 | MF442997 |
| C. hongkongensis | CBS 114828*; CPC 4670 | AY725717 | AY725667 | AY725755 | AY725622 |
| C. humicola | CBS 125251* | GQ267353 | GQ267282 | GQ267445 | GQ267233 |
| C. hurae | CBS 114551, CMW 16720 ; CPC 2344 | FJ918548 | DQ190728 | GQ267387 | AF333408 |
| C. ilicicola | CBS 190.50*; CMW 30998; IMI 299389 | AY725726 | AY725676 | AY725764 | AY725631 |
| C. indonesiae | CBS 112823*; CMW 23683; CPC 4508 | AY725718 | AY725668 | AY725756 | AY725623 |
| C. indonesiana | CBS 112936* | KX784701 | — | KX784573 | KX784631 |
| C. indusiata | CBS 144.36* | GQ267332 | DQ190653 | GQ267453 | GQ267239 |
| C. insularis | CBS 114558*; CPC 768 | FJ918556 | — | GQ267389 | AF210861 |
| C. kyotensis | CBS 114525* | AY725713 | — | AY725750 | AF348215 |
| C. lageniformis | CBS 111324*; CPC 1473 | KX784702 | — | KX784574 | KX784632 |
| C. lantauensis | CMW 47252*; CERC 3302; CBS 142888 | MF442677 | MF442792 | MF442907 | — |
| C. lateralis | CBS 136629*; CMW 31412; CERC 1747 | KJ462840 | KJ463186 | KJ463070 | KJ462955 |
| C. lauri | CBS 749.70* | GQ267312 | GQ267250 | GQ267388 | GQ267210 |
| C. leguminum | CBS 728.68* | FJ918547 | DQ190654 | GQ267391 | AF389837 |
| C. leucothoes | CBS 109166*; CPC 2385; ATCC 64824 | FJ918553 | FJ918523 | GQ267392 | FJ918508 |
| C. lichi | CERC 8866* | MF527039 | MF527055 | MF527071 | MF527097 |
| C. longiramosa | CBS 116319* | KX784705 | — | KX784577 | KX784635 |
| C. machaerinae | CBS 123183*; CPC 15378 | KX784706 | — | — | KX784636 |
| C. macroconidialis | CBS 114880*; CPC 307 | GQ267313 | — | GQ267393 | — |
| C. madagascariensis | CBS 114572*; CPC 2252 | GQ267314 | DQ190658 | GQ267394 | DQ190572 |
| C. magnispora | CBS 136249*; CMW 35184; CERC 1860 | KJ462841 | KJ463187 | KJ463071 | KJ462956 |
| C. malesiana | CBS 112752*; CPC 4223 | AY725722 | AY725672 | AY725760 | AY725627 |
| C. maranhensis | CBS 134811* | KM395861 | KM396118 | KM396035 | KM395948 |
| C. metrosideri | CBS 133603* | KC294310 | KC294308 | KC294304 | KC294313 |
| C. mexicana | CBS 110918* | FJ972526 | FJ972460 | GQ267396 | AF210863 |
| C. microconidialis | CBS 136638*; CMW 31487; CERC 1822 | KJ462845 | KJ463191 | KJ463075 | KJ462960 |
| C. montana | CERC 8952* | MF527049 | MF527065 | MF527081 | MF527107 |
| C. monticola | CBS 140645*; CPC 28835 | KT964773 | — | KT964771 | KT964769 |
| C. morganii | CBS 119670; CPC 12766; DISTEF-GP1 | GQ421797 | DQ521602 | — | DQ521600 |
| C. mossambicensis | CMW 36327* | JX570718 | JX570726 | JX570722 | — |
| C. multilateralis | CBS 110932*; CPC 957 | KX784712 | — | KX784580 | KX784642 |
| C. multinaviculata | CBS 134858*; LPF233 | KM395898 | KM396155 | KM396072 | KM395985 |
| C. multiphialidica | CBS 112678* | AY725723 | AY725673 | AY725761 | AY725628 |
| C. multiseptata | CBS 112682* | FJ918535 | DQ190659 | GQ267397 | DQ190573 |
| C. naviculata | CBS 101121 | GQ267317 | GQ267252 | GQ267399 | GQ267211 |
| C. nemoralis | CBS 116249* | KX784752 | — | KX784609 | KX784679 |
| C. nemoricola | CBS 134837* | KM395892 | KM396149 | KM396066 | KM395979 |
| C. nymphaeae | CBS 131802*; HGUP 100003 | KC555273 | — | — | JN984864 |
| C. octoramosa | CBS 111423* | KX784746 | — | KX784603 | KX784673 |
| C. orientalis | CBS 125260* | GQ267356 | GQ267285 | GQ267448 | GQ267236 |
| C. ovata | CBS 111299* | GQ267318 | GQ267253 | GQ267400 | GQ267212 |
| C. pacifica | CBS 109063*; CMW 16726; IMI 354528 | AY725724 | GQ267255 | AY725762 | GQ267213 |
| C. papillata | CBS 136097*; CMW 37976; CERC 1939 | KJ462849 | KJ463195 | KJ463079 | KJ462964 |
| C. paracolhounii | CBS 14679*; CPC 2445 | KX784714 | — | KX784582 | KX784644 |
| C. paraensis | CBS 134669*; LPF430 | KM395837 | KM396094 | KM396011 | KM395924 |
| C. parakyotensis | CBS 136085*; CMW 35169; CERC 1845 | KJ462851 | KJ463197 | KJ463081 | — |
| C. parva | CBS 110798*; CPC 410 | KX784716 | — | KX784583 | KX784646 |
| C. parvispora | CBS 111465* | KX784717 | — | KX784584 | DQ190607 |
| C. pauciramosa | CMW 5683*; CPC 971 | FJ918565 | FJ918531 | GQ267405 | FJ918514 |
| C. penicilloides | CBS 174.55*; IMI 299375 | GQ267322 | GQ267257 | GQ267406 | AF333414 |
| C. pentaseptata | CBS 136087*; CMW 35177; CERC 1853 | KJ462853 | KJ463199 | KJ463083 | KJ462966 |
| C. piauiensis | CBS 134850* | KM395886 | KM396143 | KM396060 | KM395973 |
| C. pini | CBS 123698* | GQ267344 | — | GQ267436 | GQ267224 |
| C. plurilateralis | CBS 111401*; CPC 1637 | KX784719 | — | KX784586 | KX784648 |
| C. pluriramosa | CBS 136976*; CMW 31440; CERC 1774 | KJ462882 | KJ463228 | KJ463112 | KJ462995 |
| C. polizzii | CBS 123402* | FJ972488 | FJ972438 | — | FJ972419 |
| C. propaginicola | CBS 134815*; LPF220 | KM395866 | KM396129 | KM396040 | KM395953 |
| C. pseudobrassicae | CBS 134662*; LPF280 | KM395849 | KM396106 | KM396023 | KM395936 |
| C. pseudocerciana | CBS 134824* | KM395875 | KM396132 | KM396049 | KM395962 |
| C. pseudocolhounii | CBS 127195*; CMW 27209 | HQ285816 | HQ285802 | — | HQ285788 |
| C. pseudoecuadoriae | CBS 111402*; CPC 1639 | KX784723 | — | KX784589 | KX784652 |
| C. pseudohodgesii | CBS 134818* | KM395817 | — | KM395991 | KM395905 |
| C. pseudokyotensis | CBS 137332*; CMW 31439; CERC 1774 | KJ462881 | KJ463227 | KJ463111 | KJ462994 |
| C. pseudometrosideri | CBS 134845* | KM395821 | — | KM395995 | KM395909 |
| C. pseudomexicana | CBS 130354*; DISTEF-TCROU1 | JN607296 | JN607266 | — | JN607281 |
| C. pseudonaviculata | CBS 114417*; CPC 10926 | GQ267325 | — | GQ267409 | GQ267214 |
| C. pseudopteridis | CBS 163.28*; IMI 299579 a | KM395902 | — | KM396076 | — |
| C. pseudoreteaudii | CBS 123694*; CMW 25310 | FJ918541 | FJ918519 | GQ267411 | FJ918504 |
| C. pseudoscoparia | CBS 125257* | GQ267349 | GQ267278 | GQ267441 | GQ267229 |
| C. pseudospathiphylli | CBS 109165*; CPC 1623 | FJ918562 | AF348241 | GQ267412 | FJ918513 |
| C. pseudospathulata | CBS 134841* | KM395896 | KM396153 | KM396070 | KM395983 |
| C. pseudoturangicola | CMW 474965*; CERC 7126; CBS 142890 | MF442750 | MF442865 | MF442980 | MF443080 |
| C. pseudouxmalensis | CBS 110924*; CPC 942 | KX784726 | — | — | KX784654 |
| C. pseudovata | CBS 134675*; LPF285 | KM395859 | KM396116 | KM396033 | KM395946 |
| C. pseudoyunnanensis | CMW 476555*; CERC 5376; CBS 142892 | MF442753 | MF442868 | MF442983 | MF443083 |
| C. pteridis | CBS 111793*; ATCC 34395; CPC 2372 | FJ918563 | DQ190679 | GQ267413 | DQ190578 |
| C. putriramosa | CBS 111449*; CPC 1951 | KX784728 | — | KX784591 | KX784656 |
| C. queenslandica | CBS 112146*; CPC 3213 | FJ918543 | FJ918521 | GQ267415 | AF389835 |
| C. quinqueramosa | CBS 134654*; LPF065 | KM395855 | KM396112 | KM396029 | KM395942 |
| C. reteaudii | CBS 112144*; CMW 30984; CPC 3201 | FJ918537 | DQ190661 | GQ267417 | AF389833 |
| C. robigophila | CBS 134652* | KM395850 | KM396107 | KM396024 | KM395937 |
| C. rumohrae | CBS 111431*; CPC 1716 | FJ918549 | DQ190675 | GQ267419 | AF232871 |
| C. seminaria | CBS 136632*; CMW 31450; CERC 1785; CPC 23488 | KJ462885 | KJ463231 | KJ463115 | KJ462998 |
| C. silvicola | CBS 135237* | KM395891 | — | KM396065 | KM395978 |
| C. spathiphylli | CBS 114540; ATCC 44730; CPC 2378 | GQ267330 | — | GQ267424 | AF348214 |
| C. spathulata | CBS 555.92* | GQ267331 | GQ267261 | GQ267427 | GQ267215 |
| C. sphaeropedunculata | CBS 136081*; CMW 31390; CERC 1725 | KJ462890 | KJ463236 | KJ463120 | KJ463003 |
| C. stipitata | CBS 112513*; CPC 3851 | KX784734 | — | KX784596 | KX784661 |
| C. sulawesiensis | CBS 125277* | GQ267342 | — | GQ267434 | GQ267222 |
| C. sumatrensis | CBS 112829*; CMW 23698; CPC 4518 | AY725733 | AY725696 | AY725771 | AY725649 |
| C. syzygiicola | CBS 112831*; CPC 4511 | KX784736 | — | — | KX784663 |
| C. telluricola | CBS 134664*; LPF217 | KM395843 | KM396100 | KM396017 | KM395930 |
| C. tereticornis | CBS 111301*; CPC 1429 | KX784737 | — | — | KX784664 |
| C. terrae-reginae | CBS 112151*; CPC 3202 | FJ918545 | FJ918522 | GQ267451 | FJ918506 |
| C. terrestris | CBS 136642*; CMW 35180; CERC 1856 | KJ462891 | KJ463237 | KJ463121 | KJ463004 |
| C. terricola | CBS 116247*; CPC 3583 | KX784738 | — | — | KX784665 |
| C. tetraramosa | CBS 136635*; CMW 31474*; CERC 1809*; CPC 23489 | KJ462898 | KJ463244 | KJ463128 | KJ463011 |
| C. trifurcata | CBS 112753* | KX784740 | — | KX784598 | KX784667 |
| C. tropicalis | CBS 116271; CPC 3559 | KX784742 | — | KX784599 | KX784669 |
| C. tucuruiensis | CBS 114755* | KX784743 | — | KX784600 | KX784670 |
| C. tunisiana | CBS 130357* | JN607291 | JN607261 | — | JN607276 |
| C. turangicola | CBS 136077*; CMW 31411; CERC 1746; CPC23479 | KJ462900 | KJ463246 | — | KJ463013 |
| C. uniseptata | CBS 413.67* | GQ267307 | GQ267248 | GQ267379 | GQ267208 |
| C. uxmalensis | CBS 110925*; CPC 945 | KX784708 | — | — | KX784638 |
| C. variabilis | CBS 112691; CPC 2506 | GQ267335 | GQ267264 | GQ267458 | GQ267240 |
| C. venezuelana | CBS 111052*; CPC 1183 | KX784744 | — | KX784601 | KX784671 |
| C. vietnamensis | CBS 112152* | KX784745 | — | KX784602 | KX784672 |
| C. yunnanensis | CMW 476445*; CERC 5339; CBS 14289 | MF442758 | MF442873 | MF442988 | MF443088 |
| C. zuluensis | CBS 125268; CMW 9188 | FJ972483 | FJ972433 | GQ267459 | FJ972414 |
| Curvicladiella cignea | CBS 109167*; CPC 1595; MUCL 40269 | KM231867 | KM231461 | KM231287 | KM232002 |
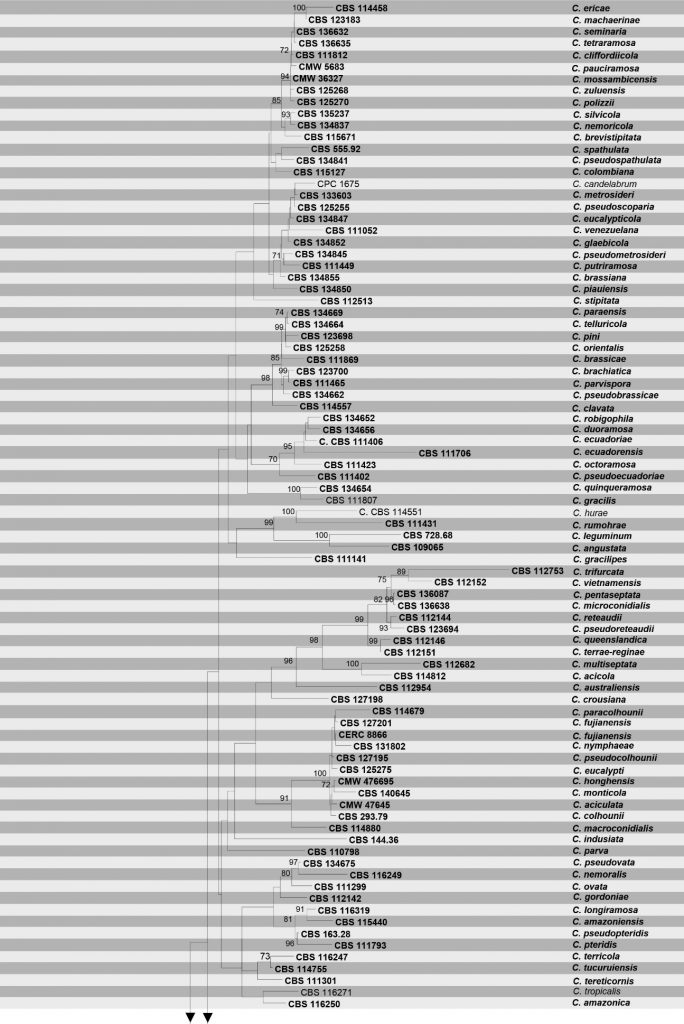
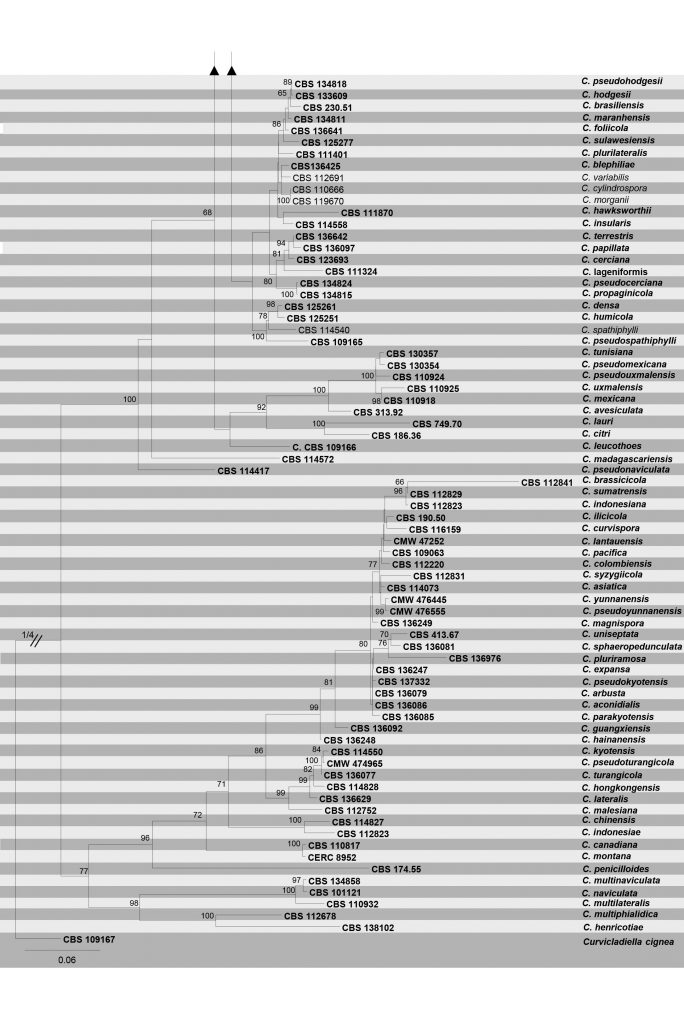
Fig Phylogenetic tree generated by maximum likelihood analysis of combined TEF1-α, TUB, cmdA and His3 sequence data of Calonectria species. Related sequences were obtained from GenBank. One hundred sixty strains are included in the analyses, which comprise 1946 characters including gaps. Tree topology of the ML analysis was similar to the one generated from BI (Figure not shown). The best scoring RAxML tree with a final likelihood value of – 35122.522366 is presented. The matrix had 1231distinct alignment patterns, with 15.02% of undetermined characters or gaps. Estimated base frequencies were as follows; A = 0.219321, C = 0.325516, G = 0.222910, T = 0.232253; substitution rates AC = 1.329187, AG = 3.755831, AT = 1.528969, CG = 0.930598, CT = 4.519462, GT = 1.000000; gamma distribution shape parameter α = 0.749195. Maximum likelihood bootstrap support (MLBT≥65%) and posterior probabilities (BIPP≥0.90) from Bayesian inference analysis are indicated respectively near the nodes. The ex-type strains are in bold and new isolates in blue. The scale bar indicates 0.06 nucleotide changes per site. The tree is rooted to Curvicladiella cignea.

No Comments