16 Oct Cytospora
Cytospora Ehrenb., Sylv. mycol. berol.: 28 (1818)
Cytospora was introduced by Ehrenberg (1818) as the type genus of the family Cytosporaceae in Diaporthales (Wehmeyer 1975; Barr 1978; Eriksson 2001; Castlebury et al. 2002). The genus is an important pathogenic fungus, causing canker and dieback on branches of a wide range of hosts with a wide distribution (Adams et al. 2005, 2006; Hyde et al. 2017, 2018; Norphanphoun et al. 2017, 2018).
Classification –Sordariomycetes, Diaporthomycetidae, Diaporthales, Valsaceae
Type species – Cytospora chrysosperma (Pers.) Fr. 1823
Distribution – Worldwide
Disease symptoms – Canker and dieback disease on branches
Hosts – Species of Abies, Acer, Berberis, Betula, Ceratonia, Cornus, Cotinus, Crataegus, Elaeagnus, Eriobotrya, Eucalyptus, Juniperus, Lumnitzera, Malus, Picea, Pinus, Platanus, Platycladus, Populus, Prunus, Pyrus, Quercus, Rosa, Salix, Sequoia, Sibiraea, Sorbaronia, Sorbus, Spiraea, Styphnolobium, Syringa, Syzygium, Tibouchina, Ulmus, Vitis and Xylocarpus (Norphanphoun et al. 2018).
Morphological based identification and diversity
Cytospora is characterized by multi-loculate conidiomata with ostiolar necks and unicellular, elongate-allantoid to subcylindrical, hyaline conidia (Fan et al. 2015a, b; Norphanphoun et al. 2017, 2018; Fig. 7). The genus which was reported as causing canker diseases in many woody plants was established in 1818 and studied in detail by taxonomists (Fries 1823; Saccardo 1884). Valsa Fr. was reported as the sexual stage of this genus and therefore, Valsa was treated as a synonym of Cytospora (1818) based on the International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (ICN, McNeill et al. 2012), with Cytospora being the oldest and most widely used name (Adams et al. 2005; Fotouhifar et al. 2010; Fan et al. 2014; Rossman et al. 2015). Previously, the conventional identification of species in Cytospora was based on their host association, often with vague morphological descriptions. Mycologists began to elucidate the relationships between Cytospora species and their hosts, with morphological observations combined with phylogenetic analyses using internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions as an effective fungal DNA barcode (Adams et al. 2005, 2006; Fotouhifar et al. 2010; Schoch et al. 2012). The establishment of multi-gene analyses using ITS, LSU, ACT, RPB2, TUB2 has proved comprehensive for the species level (Fan et al. 2015a, b, 2020; Liu et al. 2015; Yang et al. 2015; Hyde et al. 2016; Li et al. 2016; Norphanphoun 2017, 2018; Phookamsak et al. 2019).
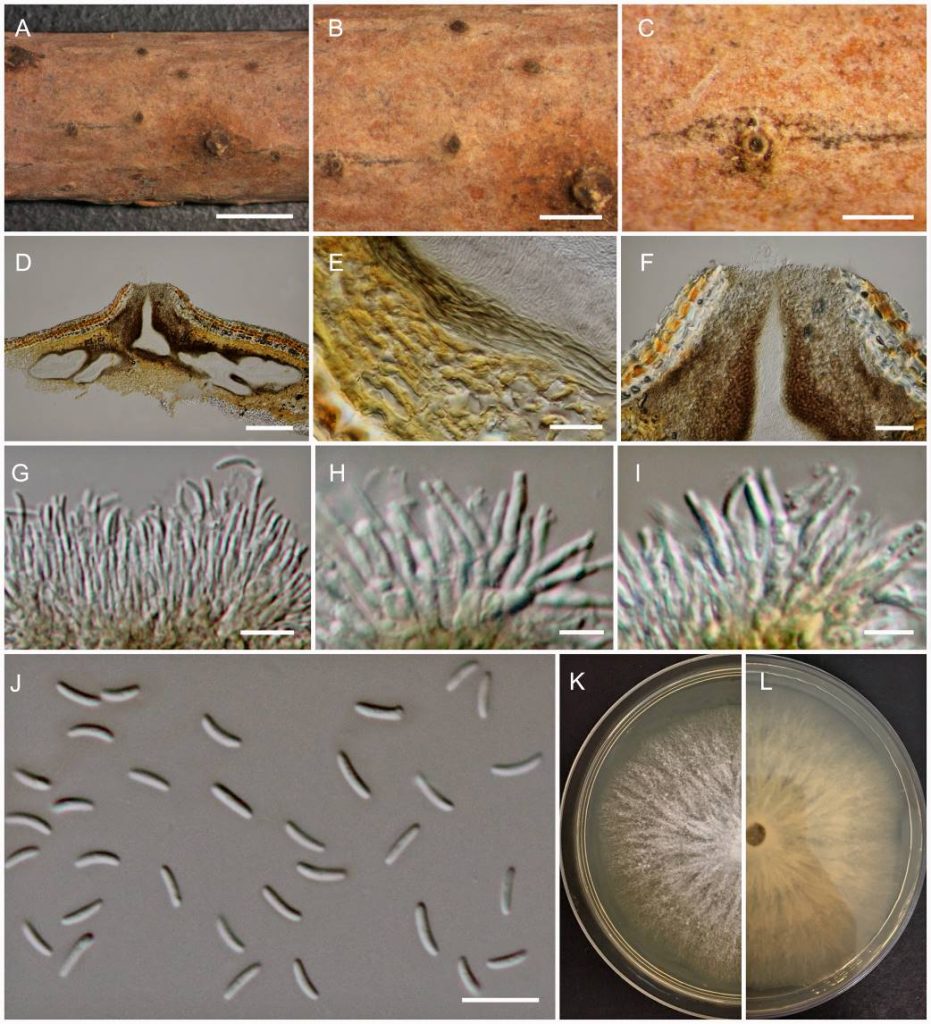
Fig. Cytospora ampulliformis a stromatal habit in wood. b fruiting bodies on the substrate. c surface of fruiting bodies. d cross-section of the stroma showing conidiomata. e peridium. f ostiolar neck. g–i Conidiogenous cells with attached conidia. j Mature conidia. k, l Colonies on MEA (k-from above, l-from below). Scale bars: a = 2 mm, b = 1 mm, c= 500 µm, d, f = 200 µm, e = 50 µm, g, h = 10 µm, i, j = 5 µm.
Molecular based identification and diversity
Comprehensive multigene phylogenetic analyses for this genus were performed by Fan et al. (2015a, b, 2020) and Norphanphoun et al. (2017, 2018).
This study reconstructs the phylogeny of Cytospora based on analyses of a combined ITS, LSU, ACT and RPB2 sequence data (Table 3, Fig 8). The phylogenetic tree is updated with recently introduced Cytospora species and corresponds to previous studies (Norphanphoun et al. 2018).
Recommended genetic markers (genus level) – LSU, ITS
Recommended genetic markers (species level) – ITS, ACT and RPB2
The accepted number of species: There are 630 species in Index Fungorum (2019) with an estimated 110 species in Kirk et al. (2008), 85 species have molecular data.
References: Fan et al. 2015a, b, Lawrence et al. 2017, Senanayake et al. 2017, 2018 (morphology), Norphanphoun et al. 2017, 2018 (morphology, phylogeny).
Table Details of Cytospora isolates used in the phylogenetic analyses. Ex-type (or ex-epitype) strains are in bold and marked with an asterisk* and voucher strains are in bold.
| Species name | Isolate no | GenBank accession numbers | |||||
| ITS | LSU | ACT | RPB2 | tef1 | TUB2 | ||
| Cytospora acaciae | CBS 468.69 | DQ243804 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. ailanthicola | CFCC 89970* | MH933618 | MH933653 | MH933526 | MH933592 | MH933494 | MH933565 |
| C. abyssinica | CMW 10181* | AY347353 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. ampulliformis | MFLUCC 16-0583* | KY417726 | KY417760 | KY417692 | KY417794 | – | – |
| C. amygdali | CBS 144233* | MG971853 | – | MG972002 | – | – | – |
| C. atrocirrhata | CFCC 89615 | KR045618 | KR045700 | KF498673 | KU710946 | KP310858 | KR045659 |
| C. austromontana | CMW 6735* | AY347361 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. beilinensis | CFCC 50493* | MH933619 | MH933654 | MH933527 | – | MH933495 | MH933561 |
| C. berberidis | CFCC 89927* | KR045620 | KR045702 | KU710990 | KU710948 | KU710913 | KR045661 |
| C. berkeleyi | StanfordT3* | AY347350 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. brevispora | CBS 116811* | AF192315 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. bungeanae | CFCC 50495* | MH933621 | MH933656 | MH933529 | MH933593 | MH933497 | MH933563 |
| C. californica | CBS 144234* | MG971935 | – | MG972083 | – | MG971645 | – |
| C. carbonacea | CFCC 89947 | MH933622 | MH933657 | MH933530 | MH933594 | MH933498 | MH933564 |
| C. carpobroti | CMW 48981* | MH382812 | MH411216 | – | – | MH411212 | MH411207 |
| C. cedri | CBS 196.50 | AF192311 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. celtidicola | CFCC 50497* | MH933623 | MH933658 | MH933531 | MH933595 | MH933499 | MH933566 |
| C. centrivillosa | MFLUCC 16-1206* | MF190122 | MF190068 | – | MF377600 | – | – |
| C. ceratosperma | CBS 116.21 | AY347335 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. ceratospermopsis | CFCC 89626* | KR045647 | KR045726 | KU711011 | KU710978 | KU710934 | KR045688 |
| C. chrysosperma | CFCC 89981 | MH933625 | MH933660 | MH933533 | MH933597 | MH933501 | MH933568 |
| C. cinerostroma | CMW 5700* | AY347377 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. cotini | MFLUCC 14-1050* | KX430142 | KX430143 | – | KX430144 | – | – |
| C. curvata | MFLUCC 15-0865* | KY417728 | KY417762 | KY417694 | KY417796 | – | – |
| C. davidiana | CXY 1350* | KM034870 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. diatrypelloidea | CMW 8549* | AY347368 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. elaeagni | CFCC 89632 | KR045626 | KR045706 | KU710995 | KF765708 | KU710918 | KR045667 |
| C. eriobotryae | IMI 136523* | AY347327 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. erumpens | MFLUCC 16-0580* | KY417733 | KY417767 | KY417699 | KY417801 | – | – |
| C. eucalypti | LSEQ | AY347340 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. eucalypticola | ATCC 96150* | AY347358 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. eucalyptina | CMW 5882 | AY347375 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. eugeniae | CMW 7029 | AY347364 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. euonymicola | CFCC 50499* | MH933628 | MH933662 | MH933535 | MH933598 | MH933503 | MH933570 |
| C. euonymina | CFCC 89993* | MH933630 | MH933664 | MH933537 | MH933600 | MH933505 | MH933590 |
| C. fraxinigena | MFLUCC 14-0868* | MF190133 | MF190078 | – | – | – | – |
| C. friesii | CBS 194.42 | AY347328 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. fugax | CBS 203.42 | AY347323 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. germanica | CXY 1322 | JQ086563 | JX524617 | – | – | – | – |
| C. gigalocus | CFCC 89620* | KR045628 | KR045708 | KU710997 | KU710957 | KU710920 | KR045669 |
| C. granati | CBS 144237* | MG971799 | – | MG971949 | – | MG971514 | MG971664 |
| C. hippophaës | CFCC 89639 | KR045632 | KR045712 | KU711001 | KU710961 | KU710924 | KR045673 |
| C. japonica | CBS 375.29 | AF191185 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. joaquinensis | CBS 144235* | MG971895 | – | MG972044 | – | MG971605 | MG971761 |
| C. junipericola | MFLU 17-0882* | MF190125 | MF190072 | – | – | MF377580 | – |
| C. juniperina | CFCC 50501* | MH933632 | MH933666 | MH933539 | MH933602 | MH933507 | – |
| C. kantschavelii | CXY 1383 | KM034867 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. kunzei | CBS 118556 | DQ243791 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. leucosperma | CFCC 89622 | KR045616 | KR045698 | KU710988 | KU710944 | KU710911 | KR045657 |
| C. longiostiolata | MFLUCC 16-0628* | KY417734 | KY417768 | KY417700 | KY417802 | – | – |
| C. longispora | CBS 144236* | MG971905 | – | MG972054 | – | MG971615 | MG971764 |
| C. lumnitzericola | MFLUCC 17-0508* | MG975778 | MH253453 | MH253457 | MH253461 | – | – |
| C. mali | CFCC 50028 | MH933641 | MH933675 | MH933548 | MH933606 | MH933513 | MH933577 |
| C. melnikii | MFLUCC 15-0851* | KY417735 | KY417769 | KY417701 | KY417803 | – | – |
| C. mougeotii | ATCC 44994 | AY347329 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. multicollis | CBS 105.89* | DQ243803 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. myrtagena | CBS 116843* | AY347363 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. nitschkii | CMW 10180* | AY347356 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. nivea | MFLUCC 15-0860 | KY417737 | KY417771 | KY417703 | KY417805 | – | – |
| C. oleicola | CBS 144248* | MG971944 | – | MG972098 | – | MG971660 | MG971752 |
| C. palm | CXY 1280* | JN411939 | – | – | – | KJ781297 | – |
| C. parakantschavelii | MFLUCC 15-0857* | KY417738 | KY417772 | KY417704 | KY417806 | – | – |
| C. parapersoonii | T28.1* | AF191181 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. parapistaciae | CBS 144506* | MG971804 | – | MG971954 | – | MG971519 | MG971669 |
| C. paratranslucens | MFLUCC 15-0506* | KY417741 | KY417775 | KY417707 | KY417809 | – | – |
| C. pini | CBS 224.52* | AY347316 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. pistaciae | CBS 144238* | MG971802 | – | MG971952 | – | MG971517 | MG971667 |
| C. platanicola | MFLU 17-0327* | MH253451 | MH253452 | MH253449 | MH253450 | – | – |
| C. platycladi | CFCC 50504* | MH933645 | MH933679 | MH933552 | MH933610 | MH933516 | MH933581 |
| C. platycladicola | CFCC 50038* | KT222840 | MH933682 | MH933555 | MH933613 | MH933519 | MH933584 |
| C. plurivora | CBS 144239* | MG971861 | – | MG972010 | – | MG971572 | MG971726 |
| C. populicola | CBS 144240* | MG971891 | – | MG972040 | – | MG971601 | MG971757 |
| C. populina | CFCC 89644 | KF765686 | KF765702 | KU711007 | KU710969 | KU710930 | KR045681 |
| C. predappioensis | MFLUCC 17-2458* | MG873484 | MG873480 | – | – | – | – |
| MFLU 17-0327 | MH253451 | MH253452 | MH253449 | MH253450 | – | – | |
| C. prunicola | MFLU 17-0995* | MG742350 | MG742351 | MG742353 | MG742352 | – | – |
| C. pruinopsis | CFCC 50034* | KP281259 | KP310806 | KP310836 | KU710970 | KP310849 | KP310819 |
| C. pruinosa | CBS 201.42 | DQ243801 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. punicae | CBS 144244 | MG971943 | – | MG972091 | – | MG971654 | MG971798 |
| C. quercicola | MFLUCC 14-0867* | MF190129 | MF190073 | – | – | – | – |
| C. rhizophorae | MUCC302 | EU301057 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. ribis | CBS 187.36 | DQ243810 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. rosae | MFLUCC 14-0845* | MF190131 | MF190075 | – | – | – | – |
| C. rostrata | CFCC 89909* | KR045643 | KR045722 | KU711009 | KU710974 | KU710932 | KR045684 |
| C. rusanovii | MFLUCC 15-0854* | KY417744 | KY417778 | KY417710 | KY417812 | – | – |
| C. salicacearum | MFLUCC 15-0509* | KY417746 | KY417780 | KY417712 | KY417814 | – | – |
| C. salicicola | MFLUCC 14-1052* | KU982636 | KU982635 | KU982637 | – | – | – |
| C. salicina | MFLUCC 15-0862* | KY417750 | KY417784 | KY417716 | KY417818 | – | – |
| C. schulzeri | CFCC 50040 | KR045649 | KR045728 | KU711013 | KU710980 | KU710936 | KR045690 |
| C. sibiraeae | CFCC 50045* | KR045651 | KR045730 | KU711015 | KU710982 | KU710938 | KR045692 |
| C. sophorae | CFCC 89598 | KR045654 | KR045733 | KU711018 | KU710985 | KU710941 | KR045695 |
| C. sophoricola | CFCC 89595* | KR045655 | KR045734 | KU711019 | KU710986 | KU710942 | KR045696 |
| C. sophoriopsis | CFCC 89600* | KR045623 | KP310804 | KU710992 | KU710951 | KU710915 | KP310817 |
| C. sorbi | MFLUCC 16-0631* | KY417752 | KY417786 | KY417718 | KY417820 | – | – |
| C. sorbicola | MFLUCC 16-0584* | KY417755 | KY417789 | KY417721 | KY417823 | – | – |
| C. spiraeae | CFCC 50049* | MG707859 | MG707643 | MG708196 | MG708199 | – | – |
| C. tamaricicola | CFCC 50508* | MH933652 | MH933687 | MH933560 | MH933617 | MH933523 | MH933588 |
| C. tanaitica | MFLUCC 14-1057* | KT459411 | KT459412 | KT459413 | – | – | – |
| C. thailandica | MFLUCC 17-0262* | MG975776 | MH253455 | MH253459 | MH253463 | – | – |
| C. tibouchinae | CPC 26333* | KX228284 | KX228335 | – | – | – | – |
| C. translucens | CXY 1351 | KM034874 | – | – | – | – | KM034895 |
| C. ulmi | MFLUCC 15-0863* | KY417759 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. valsoidea | CMW 4309* | AF192312 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. variostromatica | CMW 6766* | AY347366 | – | – | – | – | – |
| C. vinacea | CBS 141585* | KX256256 | – | – | – | KX256277 | KX256235 |
| C. viticola | CBS 141586* | KX256239 | – | – | – | KX256260 | KX256218 |
| C. xylocarpi | MFLUCC 17-0251* | MG975775 | MH253462 | MH253458 | MH253454 | – | – |
Fig Phylogenetic tree generated by maximum likelihood analysis of combined ITS, LSU, ACT and RPB2 sequence data of Cytospora species. Related sequences were obtained from GenBank. Eighty-five isolates are included in the analyses, which comprise 2756 characters including gaps. Single gene analyses were carried out and compared with each species, to compare the topology of the tree and clade stability. The tree was rooted with Diaporthe eres (AFTOL-ID 935). The tree topology of the ML analysis was similar to the MP. The best scoring RAxML tree with a final likelihood value of -8386.622374 is presented. The matrix had 388 distinct alignment patterns, with 11.83% of undetermined characters or gaps. Estimated base frequencies were as follows; A = 0.245798, C = 0.237676, G = 0.273178, T = 0.243348; substitution rates AC = 1.882600, AG = 4.123164, AT = 2.015920, CG = 0.907833, CT = 12.626910, GT = 1.000000; gamma distribution shape parameter α = 1.105097. RAxML bootstrap support values ≥70% (BT) and bayesian posterior probabilities ≥0.95 (PP) are shown respectively near the nodes. Ex-type strains are in bold.


No Comments